Blog
Get the latest insights about Compensation Management, Sales Performance, Human Resources, Pay Equity and Employee and Sales Performance.


The 3:00 AM Compensation Cycle: Burnout, Spreadsheets, and the Tradition We Refuse to Question
There is a specific kind of silence you only hear in an office at 2:47 AM. You are staring at final_v14_reallyfinal.xlsx, surrounded by cold takeout, wondering why this is the job. It’s time to ask: are we holding on to the chaos of the compensation cycle because it works, or just because it’s how we learned to prove our value?
Read more

AI Trends in Compensation: 5 Predictions for 2026 from beqom’s CEO
Gain insight into how AI is redefining compensation strategies for a more efficient, equitable, and employee-focused future in 2026.
Read more

The C-Suite’s Language: How to Win Executive Buy-In for Pay Equity and Transparency
Win executive buy-in by translating pay equity goals into C-suite language: ROI, risk reduction, and operational efficiency.
Read more

From Data Chaos to AI Confidence: Building the Right Data Foundation for AI in HR and Total Rewards
Transform HR data chaos into AI confidence with this practical four-phase roadmap for building a trusted, compliant data foundation.
Read more

The EU Gender Pay Gap
The average EU gender pay gap sits at a persistent 12%. Download our new infographic for an overview of the gender pay gap across member states and the national transposition status of the EU Pay Transparency Directive.
Read more

Employee Performance Management in a Multigenerational Workforce
Performance management systems are often broken because they fail to adapt to a multigenerational workforce. Tailoring feedback to each generation is key to motivation.
Read more

Same-Store Analysis in Compensation Spend: Bringing Financial Discipline to Rewards
Same-Store compensation analysis isolates the true impact of pay decisions by comparing spend only on employees present in both periods.
Read more

From Data to Insights: 5 Steps to Pay Equity and Transparency Success
Compliance starts with data. Prepare your employee IDs, groupings, and pay metrics now to lay a solid foundation for your pay equity and transparency analysis.
Read more

4 Ways for Hybrid, Remote, and International Companies to Master Pay Transparency
Navigating global pay transparency laws is complex, but it's a strategic opportunity. Learn how to overcome the four key challenges—from legal complexities to cultural nuances.
Read more

Humanizing Compensation: Why Pay Is More Than Just a Paycheck
Compensation is about more than just a paycheck. Discover why it's essential to humanize compensation to build trust and create a more engaged workforce.
Read more

Building Pay Transparency from the Inside Out: From Pay Philosophy to Job Postings
Pay transparency promises a more engaged and equitable workplace, but it only works when it's built into your company's core. Discover how to move beyond policy and truly integrate transparent compensation to unlock its full power.
Read more

Mastering Compensation Management in a Global Workforce
Get expert insights into global compensation strategies that scale with your workforce and drive business performance.
Read more
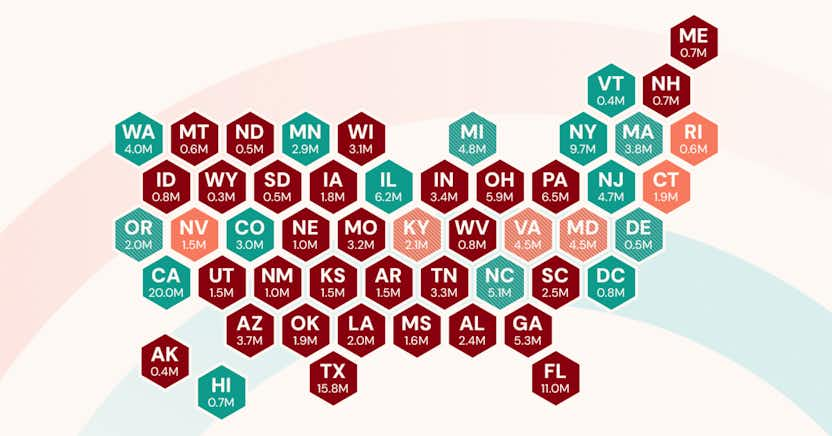
A Condensed Version of The U.S. Pay Transparency Index 2025
The U.S. Pay Transparency Index analyzes more than 13,000 job listings in the U.S. to uncover the truth behind pay transparency laws, and reveals how many companies are following the law.
Read more

How to Drive Business Results through Transparent Compensation
Elevate your compensation strategy to attract, engage, and retain top talent by embracing pay transparency.
Read more

The Strategic CHRO: A Playbook for Transformation
Discover how today's CHROs can lead transformation within organizations and shape the future of work.
Read more

Employee Turnover: The Definitive Guide to Understanding, Measuring, and Reducing It
Struggling with high employee turnover? Learn how to measure, analyze, and reduce it with proven strategies from top companies.
Read more

What’s Next in HR Technology: Compensation, Performance, and Pay Equity
Discover how HR tech advancements in compensation, performance, and pay equity can elevate your organization.
Read more

The Secret to a Smarter Comp Cycle? A Strategic Post-Mortem
Want a smoother comp cycle next year? Start with a smarter post-mortem today.
Read more

Unlocking the Power of Pay Transparency: How Global Organizations Like PUMA Are Leading the Change
See how global leaders like PUMA are turning pay transparency into a competitive advantage—and how your organization can too.
Read more
Company
About beqom
At beqom, we're on a mission to create happy, high-performing workplaces, where every individual understands their value, performs at their peak, and is rewarded fairly for their contributions.

HR Compliance
Are you struggling to navigate today's evolving compliance landscape?
Say hello to Cup of Compliance, our weekly HR compliance newsletter. Subscribe to get crisp, concise updates on regulatory shifts, key deadlines, and compliance news and start your weeks staying ahead – one sip at a time. You'll find us every Monday in your inbox!

